The Persian Empire
The Persian Empire, a series of imperial dynasties centred in Persia (modern-day Iran), spanned several centuries and played a pivotal role in shaping the ancient world.
Achaemenid Empire (550–330 BC) – The First Persian Empire
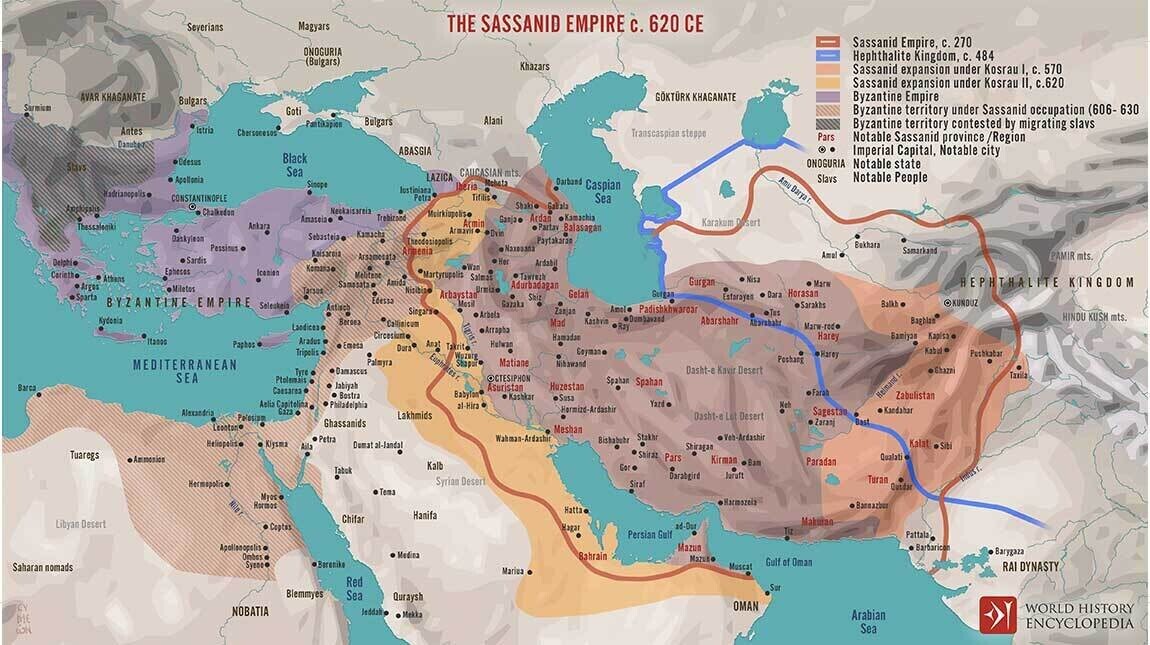
The Achaemenid Empire, founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC, was the largest empire of the ancient world, spanning three continents—from the Balkans and Eastern Europe to the Indus Valley. This powerful Persian dynasty became a model of efficient governance, cultural diversity, and religious tolerance, shaping the course of history for centuries.
A Legacy of Expansion and Innovation
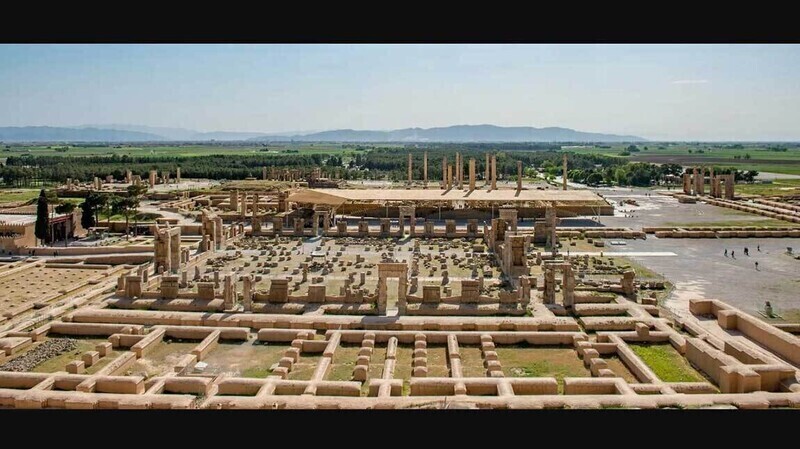
At its height under Darius I, the Achaemenid Empire extended into Central Asia and the Indian subcontinent, establishing a sophisticated administrative system that ensured stability across its vast territories. The empire was renowned for its monumental architecture, including the legendary Persepolis, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Cultural Influence and Historical Significance
The Achaemenid rulers promoted art, literature, and engineering, influencing civilizations from Greece to India. Their multicultural integration and religious freedom policies set them apart from other ancient empires.
Conquest and Enduring Influence
Despite its fall to Alexander the Great in 330 BC, the Achaemenid legacy shaped the region’s culture, governance, and architecture. Its infrastructure, law, and administration innovations laid the foundation for future civilizations and continue to be admired today.
Discover the Glory of Ancient Persia
From Persian art and symbols to the timeless elegance of Achaemenid designs, the spirit of this historic empire lives on. Explore our collection at PersianFalcon.com and own a piece of Persia’s rich heritage.
🔹 Persian Falcon – Where History Meets Modern Elegance.

Parthian Empire (247 BC–224 AD) – The Rival of Rome
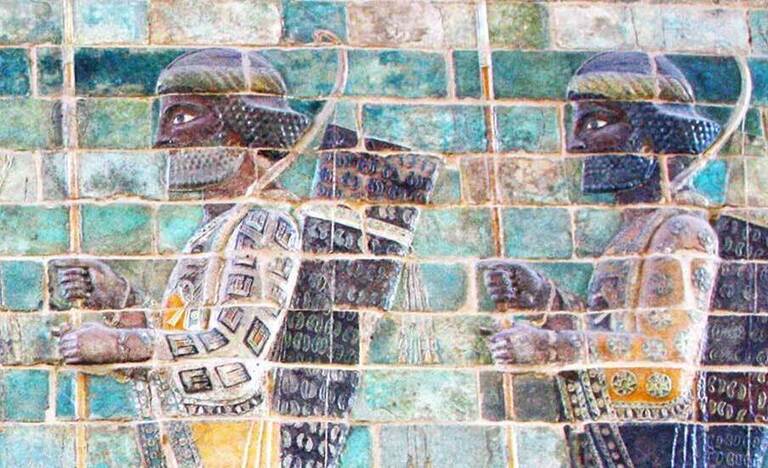
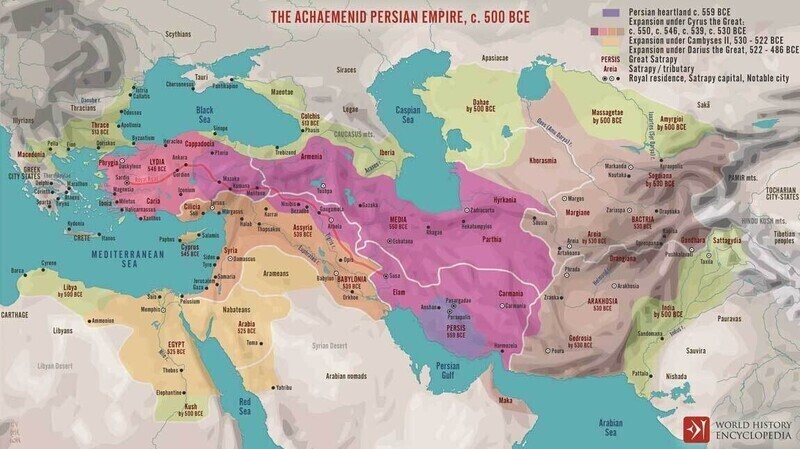
The Parthian Empire, also known as the Arsacid Empire, was a powerful Iranian dynasty that ruled from 247 BC to 224 AD, rivaling Rome for dominance in the Middle East. Famed for its skilled cavalry and archery, the Parthians mastered the legendary “Parthian Shot”—a military tactic of feigned retreat while firing arrows backward, a technique that remains iconic in military history.
A Strategic Power on the Silk Road
Located on the Silk Road, the Parthian Empire connected the Roman Empire in the West with the Han Dynasty of China, becoming a thriving center of trade and commerce. Their strategic location allowed them to control lucrative trade routes, facilitating the exchange of silk, spices, and precious goods between East and West.
Cultural Fusion – Iranian & Hellenistic Influence
The Parthians blended Greek and Iranian traditions, adopting Hellenistic art, architecture, and customs while maintaining a distinct Persian identity. This unique cultural mix is evident in their coinage, sculptures, and religious practices, showcasing an era of artistic and intellectual fusion.
The Fall & Lasting Legacy
In 224 AD, the Parthians were overthrown by the Sassanian Empire, marking the end of their reign. However, their legacy endured, influencing later Iranian dynasties and shaping Persian history for centuries to come.
Explore the Legacy of the Parthian Empire
From the warrior spirit of the Parthian cavalry to the rich cultural heritage of ancient Persia, the influence of this remarkable empire lives on. Discover Persian-inspired designs and historical symbols at PersianFalcon.com and bring a piece of ancient Persia into your collection.
🔹 Persian Falcon – Where Heritage Meets Timeless Elegance.
Sasanian Empire (224–651 AD) – The Last Great Persian Dynasty
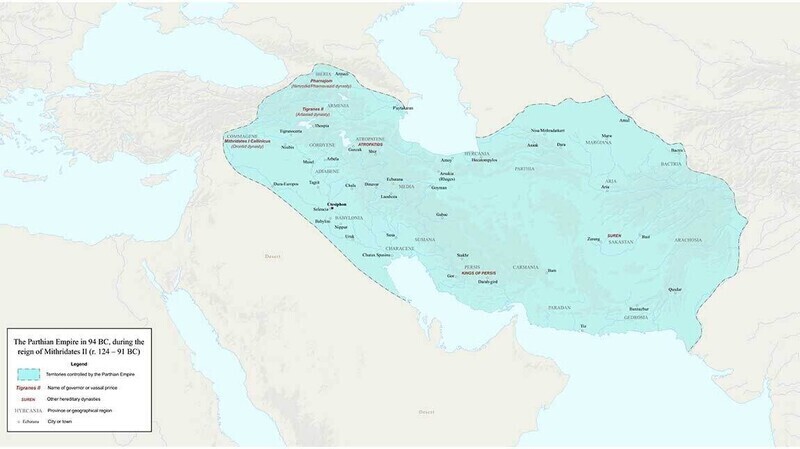
The Sasanian Empire, the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last pre-Islamic Persian empire, ruling from 224 to 651 AD. It marked a revival of Persian glory, restoring ancient traditions and establishing Zoroastrianism as the state religion. The Sassanids frequently clashed with Rome and Byzantium, leaving a powerful legacy in art, architecture, governance, and culture.
A Powerful and Centralized Empire
🏛️ Government – The Rule of the Shahanshah
The Sassanian monarch was called the Shahanshah (King of Kings), ruling over a centralized empire. Persia was divided into provinces led by governors (satraps), ensuring efficient administration.
🔥 Religion – Zoroastrianism & Persian Identity
Zoroastrianism was the official state religion, with fire temples and sacred rituals playing a vital role in society. The Sassanids promoted Persian cultural identity, preserving ancient traditions while incorporating influences from neighboring civilizations.
⚔️ Military – A Formidable Force
The Sassanian army was known for its elite heavy cavalry (cataphracts) and skilled archers, making it a formidable opponent to the Roman and Byzantine Empires. Their military innovations shaped medieval warfare for centuries.
🎨 Art & Architecture – A Golden Age
The Sassanian era was a cultural and artistic golden age, producing magnificent palaces, intricate rock reliefs, and grand temples. Their creative and architectural styles influenced later Islamic and Persian civilizations, and elements are still present in Persian designs today.
The Sassanian Legacy – A Lasting Influence
Even after the empire fell to the Arab Muslims in 651 AD, the Sassanian culture remained deeply embedded in Islamic governance, administration, and art. Their influence extended beyond Persia, shaping language, art, architecture, and political structures throughout the Middle East and Central Asia.
Discover the Glory of Ancient Persia
The Sassanian Empire’s legacy inspires Persian heritage, symbolism, and design. Explore Persian-inspired art, jewelry, and historical symbols at PersianFalcon.com and own a piece of history.
🔹 Sassanian Persia – A Legacy of Power, Culture, and Artistry.